Electronic signatures have changed the way we approach paperwork. From conducting business transactions to managing our day-to-day to-dos involving documents, signing is an integral component of our legal activities.
With an aim to reduce the use of paper for cost-effectivity and convenience, professionals and organizations have started shifting from paper to computer, adopting digital solutions in the process. Since the use of electronic signatures is now becoming a popular, go-to practice, many people are eager to learn about it. We will teach you how to collect electronic signatures or send documents for signing, but first, here are essential information about electronic signatures you need to know:
Definition of electronic signature
An electronic signature is a signature in a signature on a digital document. It may also be an image of a handwritten signature attached to an electronic document or verbal authorization in voiceprint.
A legal definition of an electronic signature, according to the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (E-SIGN) Act of the United States is “an electronic sound, symbol, or process, attached to or logically associated with a contract or other record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record.”
The legality of electronic signatures
Most of the time, before users ask how to sign electronically, they first ask if electronic signatures are legal. While not every country acknowledges the use of electronic signatures, in the United States, there are laws that govern the use of electronic signatures. Thus, making it legal.
The following are the laws that granted electronic signature the same legal status as manual, wet signatures:
E-Sign Act
The U.S. Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (E-SIGN Act) of 2000 is a federal act that facilitates the use of electronic signatures across the U.S. Based on its precepts, for an electronic signature to be valid, the person providing a signature should sign purposely and voluntarily, a consent to transact electronically should be clear, and there should be records kept in a secure online database about the signing process.
UETA
The Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) of 1999 is similar to the E-SIGN Act in terms of securing the legality of electronic contracts and the validity of electronic signatures. However, only forty-seven states recognize and implement it along with the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. The states that do not acknowledge it are Illinois, New York, and Washington.
Other e-signature laws
Here are other electronic signature laws in the U.S.:
- Illinois — Electronic Commerce Security Act
- New York — Electronic Signatures and Records Act
- Washington — Electronic Authentication Act
Now that we understand what an electronic signature is and the laws that govern it, let us discuss how to collect electronic signatures for documents.
Collecting e-signatures
Whether for online petitions or legal transactions, collecting electronic signatures is now easy through electronic signature applications.
SignedTrue is one of the trusted electronic signature solutions providers in the digital market today. Using SignedTrue, follow these steps to request electronic signatures for a PDF document:
1. Visit SignedTrue.com
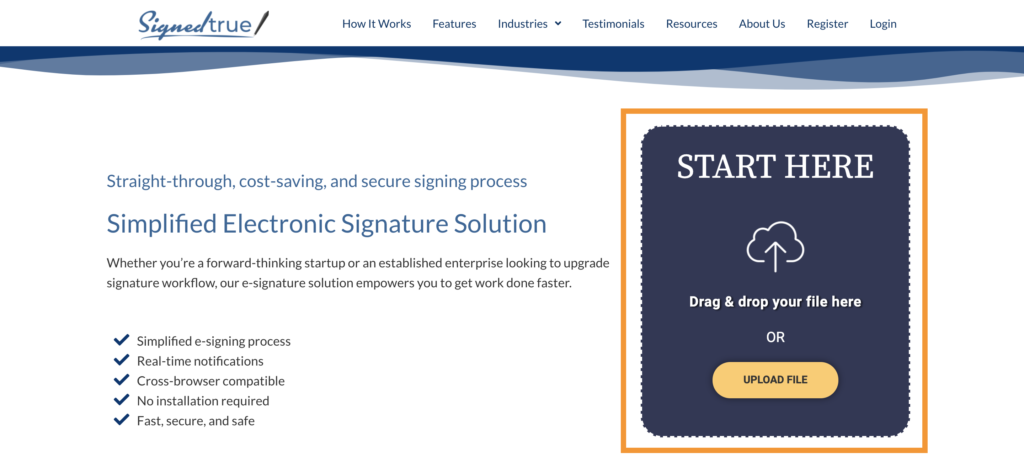
2. On the Upload Box, drag and drop your document or click on the “Upload File” button to select the file from the local storage of your device.
3. Click on the “Signature” icon to show the signing options.
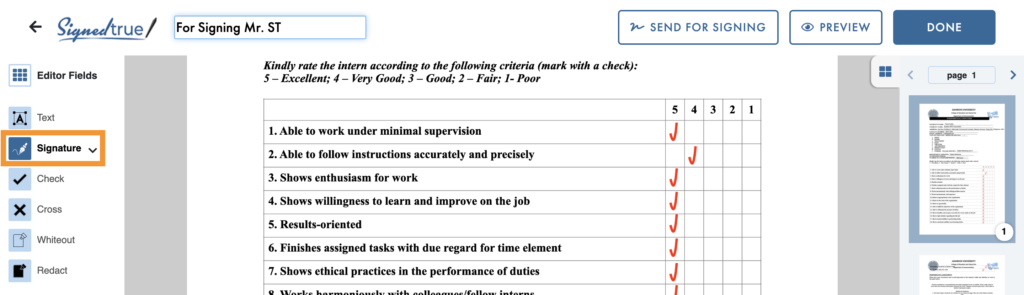
4. Click on the “Request Signature” icon.

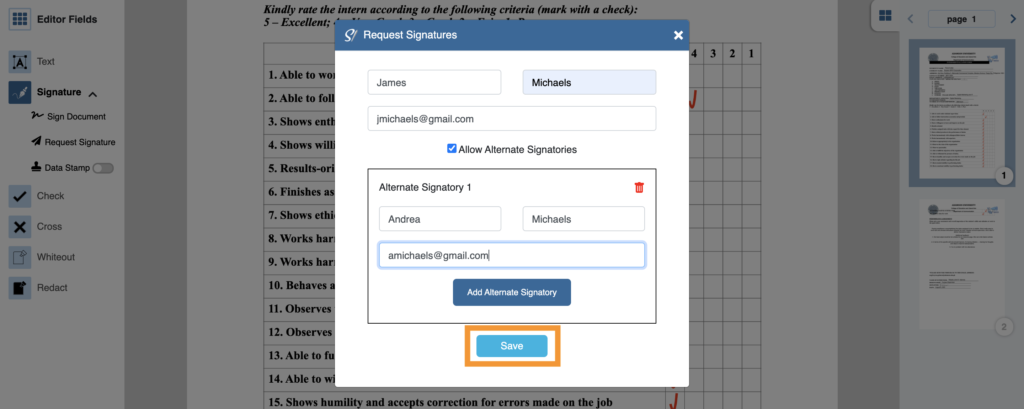
5. Enter the First Name, Last Name, and email address of the signatory. You may allow an alternate signatory by marking the “Allow Alternate Signatories” option. Then, enter the First Name, Last Name, and email of the alternate signatory.
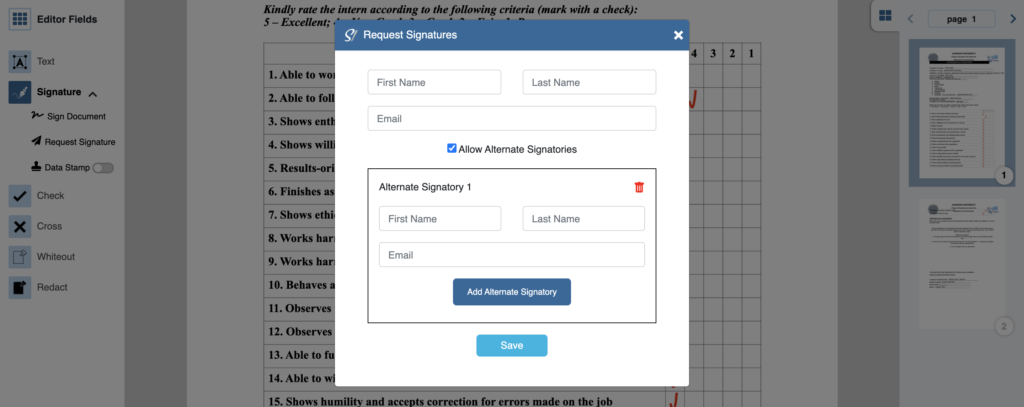
6. Click on the “Save” button.
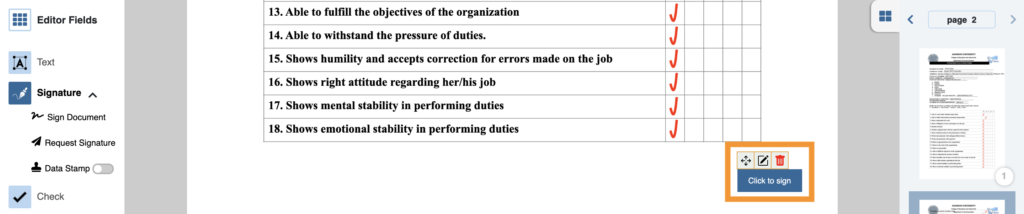
7. Position where the signatory should sign in your document.
8. Click on the “Send for Signing” button.

If you do not have an account with SignedTrue yet, you will be asked to register.
Benefits of electronic signatures
A signature is a vital element of documentation processes. Thus, integrating digital solutions into your signature workflow results in many advantages. Here are some noteworthy upsides of using electronic signatures:
Cost savings
Electronic signatures reduce, if not entirely eliminate, the use of paper and documentation costs. While the pen-and-paper method of signing may seem inexpensive, over time, the costs add up. Moreover, the traditional method of signing documents is prone to human errors and may result in wasted resources.
The use of electronic signatures reduces the cost of manual paperwork, including printing and transporting or mailing expenses.
High-level security
Perhaps the major concern of people and organizations that plan to use electronic signatures is security. A wet signature is prone to forgery and easy to tamper with, unlike an electronic signature. Electronic signatures minimize the risk of fraud and ensure the authenticity of a signature using traceable information. Providing several layers of security and authentication, electronic signatures provide electronic records or audit trails as proof of transaction and a certificate of completion for each signatory. Since there are laws that govern the use of electronic signatures, electronic signature solutions providers implement the highest levels of security and follow data security standards.
A more secure type of electronic signature, a digital signature, uses a technology called Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to verify the identity of a signer.
Convenience
A paperless workflow means documents are accessible through cloud storage. Gone are the days of digging through file cabinets just to find a specific document. Electronic signature applications enable you to sign and collect signatures no matter your location. Thus, you can transact with other individuals or organizations despite varying locations and timezones. Moreover, collaborating on a single document is easier and does not have to take a few days just to be complete, as the process takes place online. Signatories can electronically sign documents using their devices.
Faster turnaround time
Signatories can electronically sign documents in a matter of minutes, compared to the turnaround time of manual signing, which may take a few days to a few weeks, depending on the location of each signatory. Manual paperwork also involves time-consuming and tedious processes, such as scanning, printing, or transporting files. Using electronic signature applications, signatories only need to have a stable internet connection to receive and sign documents. This cuts down the documentation turnaround time significantly.

